Bitmap vs. Vector Images: Which is better for Graphic Design?
Last Updated on July 5, 2024 by Ilka Perea Hernández
An image is one of the most powerful and versatile tools a graphic designer has. In the field of computer-generated images, there are two main types: bitmap images and vector images. Find out which is better for graphic design projects: bitmap or vector images.
Being aware of the characteristics and differences between these two main types of 2D graphics is crucial to determining which type of image is better for the design project you are working on. And, on the other hand, you will be able to make a better choice of software since not all support or functions are the same with both types of graphics.
Table of Contents
- Bitmap vs. Vector Showdown
- What are the differences between Bitmap and Vector?
- Bitmap Graphics
- Vector Graphics
- Mixing Graphics
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Bitmap vs. Vector: Which one is better?
- Accuracy with reality
- Image Weight
- Resolution
- Scalability
- Software
- Ease of Usage and Application
- Bitmap vs. Vector: Which one is easier to use?
- Software and Hardware Requirements
- Formats
- Interpolation
- Vectorization and Rasterization
- The Final Product
- Bitmap vs. Vector: When should designers use them?
- When to use bitmap images
- When to use vector graphics
- Some Insights
- Bitmap vs. Vector: Which is better for Graphic Design? — Final Verdict
Bitmap vs. Vector Showdown

What are the differences between Bitmap and Vector?
Although both image types are used for similar purposes, there are marked differences that could make the designer’s job easier or turn it into a mess.

Bitmap Graphics
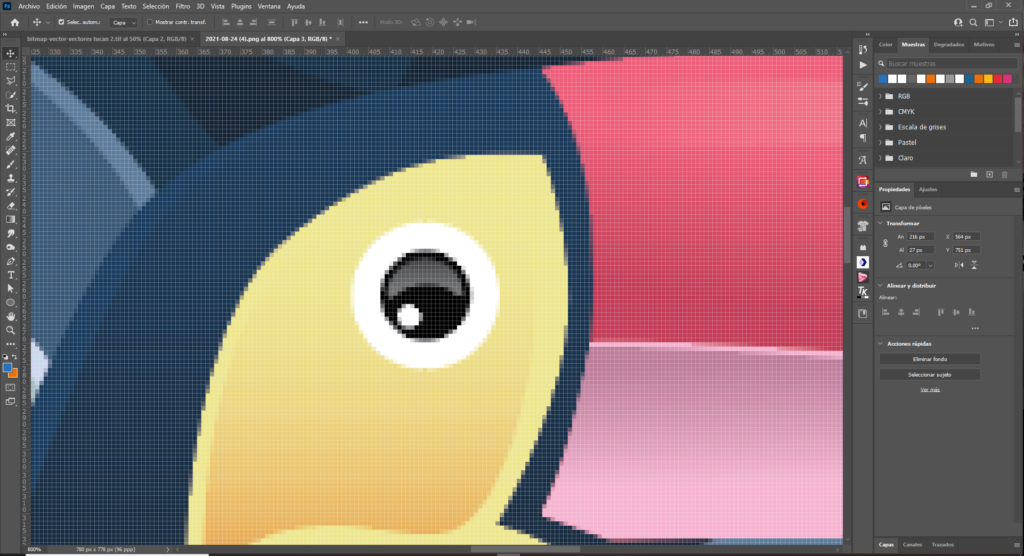
A bitmap (also called a raster) graphic is created from a grid of pixels, tiny squares of individual colors. The pixels form the image. To resume, the pixel is the minimum unit of a bitmap image. The images that appear on a computer monitor, are downloaded from the Internet, printed in communications, scanned photos, and taken by digital cameras are bitmap images.

Bitmap images are usually defined by their height and width (in pixels) and by their color depth (in bits per pixel), which determines the number of distinct colors that can be stored in each individual point and thus, to a significant extent, also the color quality of the image.

For example, a 72-dpi (dot per inch) image will weigh more than a 300-dpi image even if both are the same size in inches.

Vector Graphics
Vector images are generated by mathematical equations called Bézier Curves. The French engineer Pierre Bézier developed a technical drawing system that he first published in 1962 under the name of Bézier Curves and used in the design of the different parts of the automobile when he worked at Renault.
Vectors are made up of lines joining points in different directions and are combined to generate drawings, known as vector shapes. Using mathematical formulas, vector images can define position, shape, color, and other attributes that together create an image.

These remain editable and support the addition of fill color properties, outline, and the setting of countless effects and tools that will define the resulting graphic.
Vector images are created primarily in software. Designers cannot scan an image and save it as a vector file without using special software.
Mixing Graphics
While a bitmap image contains information about the color of each pixel, a vector graphic contains instructions on where to place each component. In this sense, it is possible to embed a bitmap graphic within a vector graphic, which is how hybrid vector and bitmap images work. However, it is not possible to embed vector information within a bitmap.
Then does this mean that a vector image is better for graphic design projects than a bitmap image?
Advantages and Disadvantages

Bitmap vs. Vector: Which one is better?
Most design projects require the use of images. Although the image is one of the most widely used graphic design concepts in composition. Its practical application requires knowledge of the strengths and weaknesses of bitmap images as well as vector graphics to choose the most suitable one for the graphic design project being worked on.
Accuracy with reality
For complex images that seek to accurately represent the details of reality, such as digital photographs, bitmap graphics are the most suitable since vector graphics do not achieve as much detail. This is because the vector graphics used solid colors for objects and the gradients do not look so real.
Image Weight
A file containing a bitmap is much larger (in terms of Megabyte) than a similar vector graphic. To give an example, if an 8″ x 8″ bitmap image has about 6MB, a vector image of the same size may have less than 1 MB. This is because each pixel stores information in that bitmap graphic, while the vector graphic is only storing mathematical coordinates.
Resolution
Vector images are resolution-independent graphics. They have soft edges and are reusable because they are independent objects that consist of lines and shapes with editable attributes such as color, fill, and outline. At the same time, they can be freely scaled without sacrificing quality. For this reason, vectors are used to create scalable working files, both on-screen and in print.
Scalability
Bitmap graphics do not have the same scalability as vector graphics and are even affected by resolution. If a bitmap graphic is enlarged, its borders will look jagged. If you shrink it, its features become blurred. When reducing the size of a bitmap image using the resampling or resizing option of the software, pixels must be discarded. On the other hand, vector graphics are redrawn to compensate for changes in resolution. The lines will remain crisp and sharp.
Software
Vector graphics are difficult to modify or even view when not opened in specialized programs. Bitmap programs, on the other hand, are more common and easier to find.
Ease of Usage and Application
Bitmap vs. Vector: Which one is easier to use?
Designing with vector graphics or bitmap images can be as easy or as difficult depending on some practical aspects such as the program being used, the formats, the capacity of the equipment available, and the type of design project being worked on.
Software and Hardware Requirements
Graphic designers require specialized software to create and modify bitmap images and vector graphics. However, it is much easier to find programs and web apps for bitmaps than for vector images.
In the same sense, software for vector files is much more robust than software that manipulates bitmaps. In other words, although vector files weigh less, the software to manage them requires more computer resources.
Bitmap images are compatible with Clip Studio Paint, Microsoft Paint, Krita, Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Lightroom, Corel Photo-Paint, Corel Paint Shop Pro, Affinity Photo, and GIMP.
Vector images are compatible with Adobe Illustrator, Corel Draw, Affinity Designer, and Inkscape.
Formats
Vector includes AI, EPS, CDR, CMX, SVG, CGM, DXF, and WMF as well as PostScript and TrueType fonts.
Bitmap includes GIF, JPG, PNG, TIFF, PSD, XBM, BMP, PCX, WEBP and bitmap fonts.
As you can see, some of the bitmap formats are more common than the specialized vector graphics files. It is worth noting that some bitmap images are created from vector tools. Previously, it was impossible to use vector graphics directly on the web, so they were transformed into formats such as GIF or PNG until browsers were updated to render SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) images. This format has become the most common and accepted format for vector images on the web.
Interpolation
When converting a vector image to PNG, GIF, or other bitmap format, designers can specify the output resolution (72 dpi, 150 dpi, 300 dpi) and the final size (pixels, inches, or centimeters) required. Once the designer converts the vector image to a bitmap, the image loses all its qualities in its vector state. It is recommended to save a copy of the vector file in its original format before converting it to a bitmap.
When graphic designers need to increase the size of a bitmap image, the software creates new pixels by estimating the color values of the new pixels based on the intensity of surrounding pixels. This process is called interpolation.
For reference, if a red pixel and a blue pixel are next to each other and the designer doubles the image resolution, two pixels will be added between them. The software and the interpolation method determine what color those added pixels will be.
Common interpolation algorithms can be grouped into two categories:
- Adaptive methods change depending on what they are interpolating.
- Non-adaptive methods treat all pixels equally.
Vectorization and Rasterization
A bitmap image can be converted into a vector image in a process called vectorization. Software such as Adobe Illustrator and Affinity Designer offer vectorization tools with results that are fully accurate to the original image. But sometimes the complexity of the image requires the process to be manual, forcing the designer to redraw the image.
Vector images can also be converted into bitmaps. This process is called rasterization. You can do it with programs such as Adobe Photoshop or GIMP which have integrated rasterization tools.
The Final Product
Graphic designers should focus on the features and advantages offered by each image format if they want to get the best out of it in the design process and production.
For example, vector images are resolution independent; this is a great advantage for web designers when creating UI elements. The sharp edges of vectors make them the most suitable format for embroidering logos on fabric.
On the other hand, bitmaps offer the highest quality and realism in digital photography as they capture greater detail due to high pixel counts.
This leads to the next question…
Bitmap vs. Vector: When should designers use them?
Here are some examples of projects where bitmap images are the best option and others where vector graphics are more suitable.
When to use bitmap images
Bitmap images are ideal for communicating realistic details, credibility, or seductive messages. For example, cookbooks use pictures of food dishes to create an appetite for the book’s readers. Tourism websites use eye-catching images of the places they promote to encourage users to travel and visit these places. Catalogs for luxury products such as jewelry, watches, or automobiles also use attractive and glamorous photographs to entice potential buyers to purchase these items.
When to use vector graphics
If the project consists of logo design, graphics for infographics, icons for signage, or 2D animations, vector images are the best choice. Thanks to the latest advances in vector software, it is also possible to create illustrations with textures and intricate details. Web designers also turn to vector graphics for their ability to scale without losing quality.
Some Insights
Graphic designers should consider the aspects and requirements of the design project before choosing to work with vector or bitmap. A poor choice will not only create practical difficulties in the design process but may also detract from the graphic message to be conveyed.
Bitmap vs. Vector: Which is better for Graphic Design? — Final Verdict
So, we can conclude that there are characteristics that make bitmap images different from vector graphics. Depending on the project they are working on, each image format can be useful for graphic designers. So, neither is “better” than the other.
Share
Spread the love… and this post!
If you liked it, share this post on your social networks. Smart designers share good things with others.

Bibliography
- Dabner, D., Stewart, S., Vickress, A. (2020). Graphic Design School: The Principles and Practice of Graphic Design (7th ed.). Wiley.
- Gómez-Palacio, B.; Vit, A. (2011). Graphic Design Referenced: A Visual Guide to the Language, Applications, and History of Graphic Design. Rockport Publishers.
- Leborg, C. (2006). Visual Grammar: A Design Handbook (Visual Design Book for Designers, Book on Visual Communication). Princeton Architectural Press.
- Malamed, C. (2009). Visual Language for Designers: Principles for Creating Graphics That People Understand. Rockport Publishers.
- Poulin, R. (2018). The Language of Graphic Design Revised and Updated: An illustrated handbook for understanding fundamental design principles. Rockport Publishers.

